Building muscle mass is a common goal for fitness enthusiasts all over the world. Whether you’re aiming for a stronger physique, better athletic performance, or improved overall health, understanding the science behind muscle growth can help you achieve your goals faster.
This comprehensive guide explores how muscles grow and the key role played by exercise, diet, and sleep. By the end, you’ll have a clear roadmap to optimize your muscle-building efforts.

Understanding Muscle Growth (Hypertrophy)
Muscle growth, or hypertrophy, is the process by which muscle fibers increase in size due to repeated stress from resistance training. When you lift weights or perform bodyweight exercises, tiny tears occur in your muscle fibers. The body repairs these tears, making the muscles thicker and stronger over time.
Muscle growth is influenced by three critical factors:
- Mechanical Tension – Created when you lift heavy weights, forcing muscles to adapt.
- Muscle Damage – Micro-tears in muscle fibers that lead to repair and growth.
- Metabolic Stress – The buildup of metabolites such as lactic acid, which triggers a growth response.
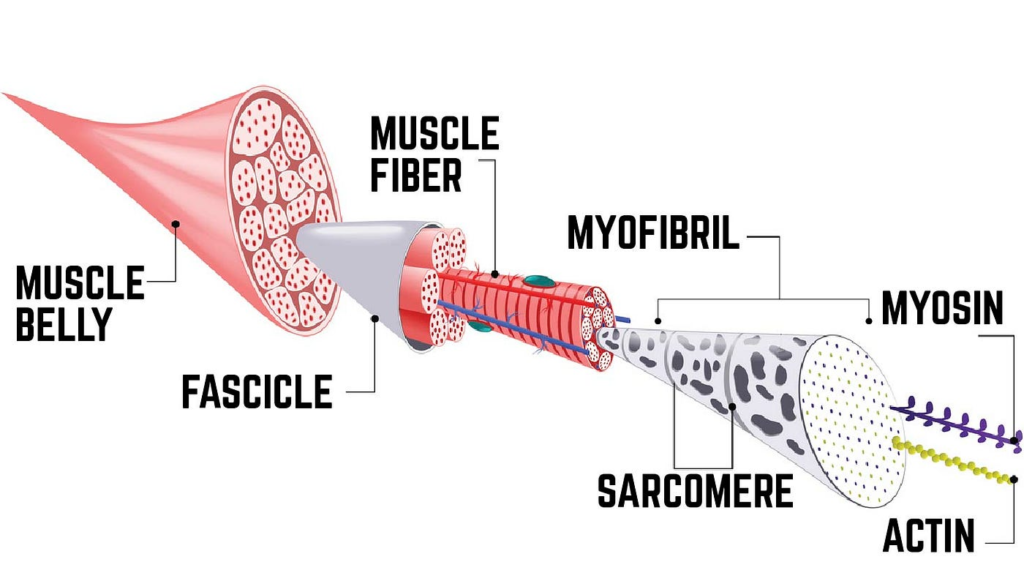
The Muscle Growth Process: Human Anatomy Perspective
When you perform resistance exercises, the following process takes place in your body:
- Muscle Contraction: Your muscles contract during weightlifting, activating motor units and muscle fibers.
- Micro-Trauma: Microscopic tears occur in the muscle fibers due to mechanical tension.
- Inflammatory Response: The body triggers an immune response to repair the damage by increasing blood flow and delivering nutrients.
- Satellite Cells Activation: These specialized muscle stem cells fuse to damaged fibers, adding new nuclei to the muscle, leading to growth.
- Protein Synthesis: Amino acids from your diet are used to rebuild stronger muscle fibers.
- Adaptation: Over time, your muscles adapt to stress, becoming bigger and stronger with consistent training.
1. Exercise: Building Muscle Through Training
Why Exercise Matters for Muscle Growth
Without resistance training, your muscles won’t experience the necessary stress to grow. Exercise stimulates muscle protein synthesis (MPS), a process in which your body builds new muscle tissue.
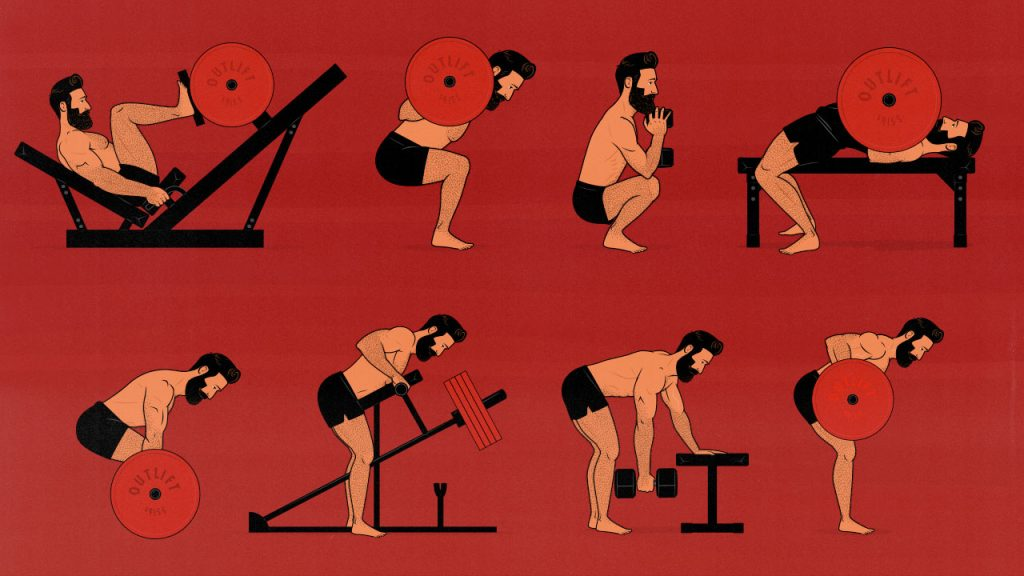
Best Exercises for Muscle Growth
To maximize hypertrophy, include a mix of compound and isolation exercises in your routine.
Compound Exercises (Multi-Joint Movements)
These exercises target multiple muscle groups simultaneously, helping you lift heavier and burn more calories.
- Squats – Builds legs, glutes, and core.
- Deadlifts – Engages the back, hamstrings, and core.
- Bench Press – Works the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
- Pull-Ups/Chin-Ups – Strengthens the back and arms.
Isolation Exercises (Single-Joint Movements)
These movements focus on a specific muscle, helping to enhance definition and size.
- Bicep Curls – Targets the biceps for arm growth.
- Triceps Extensions – Builds the back of the arms.
- Leg Curls – Isolates the hamstrings.
- Calf Raises – Strengthens the lower legs.
Workout Split for Muscle Growth
Here’s a proven weekly workout split for maximum hypertrophy:
- Day 1: Chest & Triceps
- Day 2: Back & Biceps
- Day 3: Legs & Core
- Day 4: Shoulders & Arms
- Day 5: Full-Body or Rest
- Day 6: Cardio + Core
- Day 7: Rest
Progressive Overload: The Key to Growth
Progressive overload is the gradual increase in stress placed on the muscles. It ensures continuous growth by:
- Increasing the weight lifted over time.
- Performing more repetitions or sets.
- Reducing rest periods to boost intensity.

2. Diet: Nutrition Strategies for Muscle Growth
Your diet plays a crucial role in providing the nutrients needed for muscle recovery and growth. Without the right balance of macronutrients and micronutrients, your progress will stall.
Macronutrients for Muscle Gain
- Protein:
- Essential for muscle repair and growth.
- Daily Target: 1.6-2.2 grams per kg of body weight.
- Best Sources:
- Animal-based: Chicken, fish, eggs, dairy.
- Plant-based: Lentils, chickpeas, soy.
- Carbohydrates:
- Provide energy for workouts and recovery.
- Daily Target: 4-6 grams per kg of body weight.
- Best Sources:
- Complex Carbs: Oats, quinoa, whole grains.
- Simple Carbs: Fruits, honey, rice.
- Fats:
- Support hormone production (testosterone).
- Daily Target: 20-30% of total calorie intake.
- Best Sources:
- Healthy Fats: Nuts, seeds, avocado, olive oil.
- Omega-3s: Fish oil, flaxseeds.

3. Sleep: The Ultimate Muscle Recovery Tool
Sleep is often neglected in fitness plans, but it plays a critical role in muscle recovery and growth. During deep sleep, your body releases growth hormones that help repair damaged tissues and build stronger muscles.
How Sleep Enhances Muscle Growth
- Hormonal Balance: Growth hormone and testosterone peak during deep sleep cycles.
- Muscle Repair: Protein synthesis increases while muscle breakdown decreases.
- Energy Restoration: Glycogen stores replenish, fueling future workouts.
- Mental Recovery: Improved focus and motivation for training sessions.
Tips for Better Sleep
- Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night.
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule.
- Avoid screen time before bed.
- Create a dark, cool, and quiet sleep environment.
- Reduce caffeine intake in the evening.

Conclusion: The Perfect Formula for Muscle Growth
Achieving optimal muscle growth requires a balanced combination of:
- Consistent exercise with progressive overload.
- Proper diet rich in protein, carbs, and healthy fats.
- Sufficient sleep to allow muscle recovery and repair.
By following these guidelines, you’ll be on your way to building stronger, leaner muscles effectively.
Start your journey today and unlock your full potential!




