3d illustration of a cancer cell and lymphocytes
Understanding Cancer Types, Tumors, Chemotherapy, Ayurvedic Approaches, and Technological Advancements
Cancer remains one of the most challenging and multifaceted diseases of our time. With millions affected globally, the journey from diagnosis to treatment involves a myriad of strategies—from conventional chemotherapy to integrative approaches such as Ayurveda, and even cutting-edge technological innovations. We mention here the importance of understanding the different types of cancer, the nature of tumors, the benefits and limitations of chemotherapy, and how ancient Ayurvedic practices are being revisited alongside modern technology to combat cancer.
In this blog, we explore these dimensions in detail to provide an engaging, easy-to-read guide that will help you better understand the current and emerging landscape of cancer treatment.
1. Understanding the Various Types of Cancer
What Is Cancer?
Cancer is a group of diseases characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and division. Unlike normal cells, which follow strict rules regarding growth and death, cancer cells ignore these signals, proliferating uncontrollably. This can lead to the formation of masses known as tumors or, in the case of blood cancers, abnormal cell accumulation in the blood or bone marrow.
Major Categories of Cancer
While there are over 100 different types of cancer, they can be broadly categorized into a few groups:
- Carcinomas:
- Description: These cancers originate in the epithelial cells that line organs and tissues.
- Examples: Breast, lung, colon, and prostate cancers.
- Sarcomas:
- Description: These originate in the connective tissues, such as bone, cartilage, and muscle.
- Examples: Osteosarcoma (bone cancer) and soft tissue sarcomas.
- Leukemias:
- Description: Cancers of the blood-forming tissues, leading to the production of abnormal blood cells.
- Examples: Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
- Lymphomas:
- Description: These affect the lymphatic system, which is part of the body’s immune system.
- Examples: Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma.
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Cancers:
- Description: These affect the brain and spinal cord.
- Examples: Glioblastoma multiforme and astrocytomas.
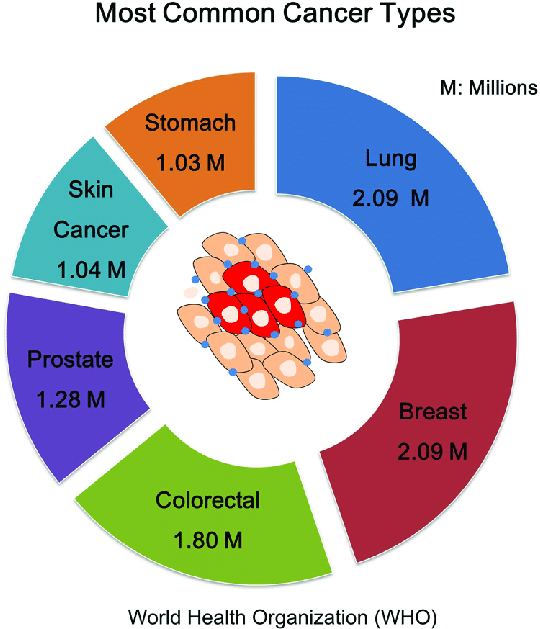
Noteworthy Statistics and Trends
The video emphasized the importance of early detection and awareness. Key takeaways include:
- Early Diagnosis Improves Outcomes: Detecting cancer at an early stage can significantly enhance treatment efficacy.
- Varied Incidence Rates: Certain cancers, such as lung cancer in smokers and breast cancer in women, have higher incidence rates, prompting targeted screening programs.
The Role of Lifestyle and Genetics
While environmental factors like smoking, diet, and exposure to radiation contribute to the development of cancer, genetics also play a pivotal role. Family history and inherited mutations (e.g., BRCA1 and BRCA2 for breast cancer) are critical markers that can predispose individuals to certain cancer types.
2. Tumors: The Heart of the Matter
What Is a Tumor?
A tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue that forms when cells grow and divide more than they should or do not die when they should. However, not all tumors are cancerous.
Benign vs. Malignant Tumors
It is essential to differentiate between benign and malignant tumors:
| Characteristic | Benign Tumors | Malignant Tumors (Cancerous) |
|---|---|---|
| Growth Rate | Slow-growing | Rapid and aggressive |
| Invasiveness | Do not invade surrounding tissues | Invade and destroy nearby tissues |
| Spread (Metastasis) | Do not spread to other parts of the body | Can metastasize to distant organs |
| Recurrence | Rarely recur after removal | High recurrence rates even after treatment |
| Impact on Health | Generally less harmful; may cause problems if large or in sensitive areas | Often life-threatening if not treated promptly |
Tumor Grading and Staging
Understanding a tumor’s grade and stage is crucial for planning treatment:
- Grading: Refers to how much the cancer cells differ from healthy cells under a microscope. A higher grade indicates more abnormality and aggressive behavior.
- Staging: Indicates the extent of cancer spread. Common staging systems include the TNM system (Tumor size, Node involvement, Metastasis).
Not all tumors are created equal—factors such as location, size, genetic markers, and the patient’s overall health are integral in tailoring therapy. This approach leads to more precise and effective treatment strategies.
3. Chemotherapy: The Conventional Approach to Cancer Treatment
How Chemotherapy Works
Chemotherapy is one of the oldest and most widely used cancer treatments. It involves the use of drugs designed to kill rapidly dividing cells, which includes cancer cells. However, because these drugs also affect healthy rapidly dividing cells (like those in hair follicles and the digestive tract), side effects are common.
Types of Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy can be classified based on several factors:
- Adjuvant Chemotherapy:
Administered after surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. - Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy:
Given before surgery to shrink tumors, making them easier to remove. - Combination Chemotherapy:
Utilizes more than one drug simultaneously to target cancer cells through different mechanisms.
Common Chemotherapy Drugs
Below are some examples of widely used chemotherapy drugs:
- Doxorubicin:
Used for a variety of cancers including breast cancer and lymphomas. - Cisplatin:
Often employed for lung, ovarian, and testicular cancers. - Cyclophosphamide:
Commonly used in breast cancer and lymphomas. - Paclitaxel:
Used for ovarian, breast, and lung cancers.
Side Effects and Management
Chemotherapy is notorious for its side effects. Here’s a list of common issues and possible management strategies:
- Nausea and Vomiting:
Anti-emetic drugs and dietary adjustments. - Hair Loss:
Often temporary; scalp cooling caps may reduce severity. - Fatigue:
Light exercise and rest can help manage energy levels. - Immune Suppression:
Close monitoring and prophylactic antibiotics can prevent infections.
While chemotherapy remains a cornerstone in cancer treatment, its one-size-fits-all nature can be limiting. Personalizing chemotherapy regimens and integrating them with other treatment modalities can lead to better outcomes and reduced side effects.
4. Ayurvedic Approaches: Ancient Wisdom in Modern Cancer Care
An Overview of Ayurveda
Ayurveda, a traditional Indian system of medicine, offers a holistic approach to health and healing. With roots tracing back over 5,000 years, Ayurveda emphasizes balance among the body, mind, and spirit. It is increasingly being explored as a complementary therapy for managing cancer.
Ayurvedic Principles in Cancer Management
The Ayurvedic approach to cancer is centered around restoring the body’s natural equilibrium. Key components include:
- Herbal Remedies:
Natural herbs are used to boost immunity and support the body’s healing processes. - Diet and Nutrition:
Customized dietary plans aim to reduce toxins (ama) and strengthen the digestive fire (agni). - Lifestyle Modifications:
Practices such as yoga, meditation, and pranayama (breathing exercises) help manage stress and enhance overall wellbeing. - Detoxification:
Panchakarma, a series of detoxification procedures, is often recommended to cleanse the body.
Examples of Ayurvedic Herbs and Formulations
Several herbs have shown promise in complementary cancer care. Here are some notable examples:
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa):
- Active Compound: Curcumin
- Benefits: Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti-proliferative properties.
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera):
- Benefits: Reduces stress, enhances immune function, and may inhibit cancer cell growth.
- Neem (Azadirachta indica):
- Benefits: Known for its anti-inflammatory and detoxifying properties.
- Tulsi (Holy Basil):
- Benefits: Supports immune function and has been used traditionally for its healing properties.
- Amla (Indian Gooseberry):
- Benefits: Rich in vitamin C and antioxidants, aiding in detoxification and cell protection.
Integrating Ayurveda with Conventional Treatments
The video highlighted that Ayurveda should not be seen as a replacement for conventional cancer treatments but rather as a complementary approach. Integrating Ayurvedic principles with chemotherapy or radiotherapy can potentially:
- Reduce Side Effects:
Herbal supplements and dietary changes may help mitigate the harsh side effects of chemotherapy. - Enhance Quality of Life:
Stress reduction techniques and detoxification processes can improve overall wellbeing. - Boost Immunity:
Strengthening the body’s natural defenses may improve recovery and resilience during treatment.

5. Technological Advancements in Cancer Treatment
Precision Medicine and Targeted Therapy
In recent years, the field of oncology has witnessed significant technological advancements. Precision medicine tailors treatment based on the genetic makeup of the individual and the tumor. This involves:
- Genomic Profiling:
Identifying mutations and genetic alterations in cancer cells to select the most effective targeted therapies. - Targeted Drugs:
Medications designed to interfere with specific molecular targets associated with cancer growth.
Immunotherapy: Harnessing the Body’s Own Defenses
Immunotherapy has emerged as a breakthrough treatment, empowering the immune system to fight cancer more effectively. Key modalities include:
- Checkpoint Inhibitors:
Drugs that block proteins used by cancer cells to evade immune detection (e.g., PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors). - CAR-T Cell Therapy:
Engineering a patient’s T cells to recognize and attack cancer cells. - Cancer Vaccines:
Stimulating the immune system to recognize and target cancer-specific antigens.
Robotic Surgery and Minimally Invasive Techniques
The advent of robotic-assisted surgery has revolutionized cancer treatment by allowing for:
- Precision:
Enhanced accuracy in removing tumors while preserving healthy tissue. - Reduced Recovery Time:
Minimally invasive techniques lead to shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery. - Better Outcomes:
Lower complication rates and improved cosmetic results in surgeries such as prostatectomy and hysterectomy.
Nanotechnology and Liquid Biopsy
Nanotechnology is opening new frontiers in cancer care:
- Nanoparticles:
Designed to deliver drugs directly to the tumor site, thus minimizing systemic side effects. - Liquid Biopsy:
A minimally invasive technique that detects cancer cells or DNA fragments in the blood, allowing for early detection and monitoring of treatment response.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Oncology
AI and machine learning are being integrated into cancer care to:
- Enhance Diagnosis:
AI algorithms can analyze imaging data more accurately and quickly than traditional methods. - Predict Treatment Response:
Machine learning models can forecast how a patient might respond to a particular treatment, aiding in personalized care plans. - Optimize Clinical Trials:
AI assists in identifying suitable candidates and predicting outcomes, which accelerates the development of new therapies.

The technology is rapidly transforming cancer treatment by offering more targeted, efficient, and less invasive options. The fusion of traditional methods with modern innovations is paving the way for a future where cancer care is highly personalized and remarkably effective.
6. Comparative Analysis: Conventional vs. Ayurvedic vs. Technological Approaches
To better understand the diverse treatment options available, let’s take a closer look at a comparative table:
| Aspect | Conventional (Chemotherapy/Radiotherapy) | Ayurvedic Approach | Technological Advancements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | Targets rapidly dividing cells with cytotoxic drugs | Uses herbs, diet, and lifestyle to restore balance | Targets specific molecular pathways and utilizes precision tools |
| Treatment Focus | Direct destruction of cancer cells | Enhancing body’s immunity and overall health | Precision, early detection, and personalized care |
| Side Effects | Often significant (nausea, hair loss, fatigue) | Generally milder; focuses on holistic healing | Reduced due to targeted action; minimally invasive |
| Integration with Other Modalities | Often used in combination with surgery or radiation | Typically complementary to conventional treatments | Can be combined with conventional and integrative approaches |
| Examples | Doxorubicin, Cisplatin, Paclitaxel | Turmeric, Ashwagandha, Neem, Tulsi, Amla | CAR-T Cell Therapy, Nanoparticle Drug Delivery, AI Diagnostics |
| Cost and Accessibility | Variable; high cost in some regions | Often cost-effective; based on natural products | Emerging; may initially be high cost but expected to decrease with scale |
This table highlights that no single approach holds all the answers. The future of cancer treatment likely lies in a multidisciplinary strategy that integrates conventional therapies with both ancient wisdom and cutting-edge technology.
7. Embracing a Holistic Approach to Cancer Management
The Need for Personalized Treatment
One of the key themes from the video is the importance of personalized medicine. Every patient is unique, and a treatment plan that works for one person might not be as effective for another. By combining:
- Conventional Methods:
Such as chemotherapy and radiotherapy for their proven efficacy. - Ayurvedic Practices:
To bolster overall health, manage side effects, and improve quality of life. - Technological Innovations:
For precise diagnosis, monitoring, and targeted therapy.
Doctors can tailor a comprehensive treatment strategy that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of cancer care.
Patient Empowerment and Informed Decisions

Empowering patients through education is paramount. When patients understand their disease and the spectrum of available treatments, they can make informed decisions in collaboration with their healthcare providers. Here are some tips for patients navigating cancer treatment:
- Ask Questions:
Inquire about the rationale behind each treatment option. - Research:
Use reputable sources to learn about conventional, Ayurvedic, and technological treatments. - Seek Second Opinions:
Don’t hesitate to consult multiple experts to find the best care plan. - Focus on Overall Wellness:
Incorporate stress management techniques, balanced nutrition, and regular physical activity.
Future Directions in Cancer Care
The landscape of cancer treatment is continuously evolving. Emerging areas of research include:
- CRISPR and Gene Editing:
Targeting genetic mutations at their source to prevent cancer progression. - Biomarker Discovery:
Identifying new biomarkers for early detection and treatment monitoring. - Integration of Data Analytics:
Using big data and AI to optimize treatment protocols and predict patient outcomes.
As these innovations mature, the integration of diverse treatment methodologies will likely become standard practice, leading to more personalized and effective care.
Conclusion
The fight against cancer is multifaceted, demanding a blend of time-tested practices and modern innovations. By understanding the various types of cancer and the nature of tumors, patients and clinicians can better appreciate the rationale behind different treatment strategies. While chemotherapy remains a cornerstone of conventional care, the resurgence of Ayurvedic approaches—with their focus on balance and holistic healing—offers a promising complementary path. Meanwhile, the rapid pace of technological advancements such as precision medicine, immunotherapy, and AI-driven diagnostics is transforming how we approach cancer treatment.
In summary:
- Understanding Cancer Types and Tumors:
A strong grasp of the diversity and behavior of cancer is essential for effective treatment planning. - Conventional Chemotherapy:
While effective, it often requires personalization to minimize side effects. - Ayurvedic and Integrative Approaches:
These offer natural, supportive therapies that can enhance overall wellness and complement standard treatments. - Technological Innovations:
They hold the promise of more precise, less invasive, and highly targeted therapies that can improve patient outcomes.
This comprehensive approach, as highlighted in the video and explored throughout this blog, encourages us to think beyond conventional silos. Whether you are a patient, caregiver, or simply interested in medical advancements, staying informed about these evolving modalities is critical. The future of cancer treatment is bright—an amalgamation of ancient wisdom and modern technology working together to offer hope, healing, and improved quality of life for those affected by cancer.
By embracing a holistic and patient-centric approach, the evolving landscape of cancer care offers renewed hope in the battle against this formidable disease. Stay informed, stay empowered, and together we can contribute to a future where cancer is not just managed, but eventually conquered.
For further insights and updates on cancer treatment innovations, subscribe to our newsletter and follow our blog. Your journey towards understanding cancer care begins with knowledge—and every step forward is a step towards a healthier future




